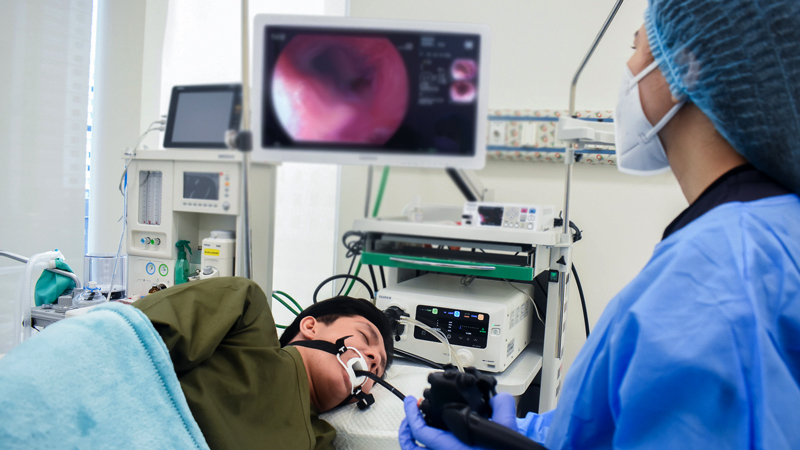
Gastroscopy
A gastroscopy, also known as an upper endoscopy, is a medical procedure used to visually examine the lining of the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum (the first part of the small intestine).
During a gastroscopy, a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope is inserted through the mouth and guided down the throat into the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The endoscope contains a small camera and light, which allows the doctor to see the inner lining of these organs on a monitor in real time.
Gastroscopy is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as ulcers, inflammation, bleeding, tumors, or other abnormalities in the upper digestive tract. It can also be used to take tissue samples (biopsies) for further examination or to treat certain conditions, such as removing polyps or stopping bleeding.
The procedure is usually performed under sedation to make the patient more comfortable, and it typically takes only a few minutes to complete. Afterward, patients may experience some temporary discomfort, such as a sore throat or bloating, but these symptoms usually resolve quickly.
